It's important to note that these boards aren't limited to just LCD panels—they're also essential for driving OLED and LED displays.

6.5 inch flexible OLED with HDMI Board
For example, consider a 6.5-inch flexible OLED panel with a MIPI interface. Below is the pin assignment for this type of panel,
1-ELVSS 2 -TP-SDA 3-ELVSS 4-TP-INT 5-MTP-PWR 6-TP-SCL 7-ELVDD 8-TP-VDD 9-ELVDD 10-TP-IOVCC
11-AVDD 12-TP-RST(NC) 13-VDDI 14-GND 15-VCI 16-D2P 17-NC 18-D2N 19-AVDD-EN 20-DIP
21-SWIRE 22-DIN 23-TE 24-GND 25-RST 26-CLKP 27-NC 28-CLKN 29-GND 30-GND
31-NC 32-DOP 33-NC 34-DON 35.NC 36-D3P 37-NC 38-D3N 39-NC 40-GND
11-AVDD 12-TP-RST(NC) 13-VDDI 14-GND 15-VCI 16-D2P 17-NC 18-D2N 19-AVDD-EN 20-DIP
21-SWIRE 22-DIN 23-TE 24-GND 25-RST 26-CLKP 27-NC 28-CLKN 29-GND 30-GND
31-NC 32-DOP 33-NC 34-DON 35.NC 36-D3P 37-NC 38-D3N 39-NC 40-GND
Panox Display has been supplying LCD and OLED displays for many years. For clients who prefer not to handle the complexities of driving a display panel themselves, we offer customized display controller boards. Our service features competitive pricing, fast development cycles, and quick production turnaround. Click here to learn more about our custom controller board solutions.
The following is a standard HDMI interface pin assginment,
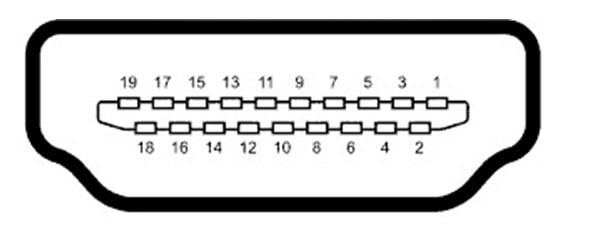
1 TMDS Data Channel 2+
2 TMDS Data Channel 2 Shield
3 TMDS Data Channel 2-
4 TMDS Data Channel 1+
5 TMDS Data Channel 1 Shield
6 TMDS Data Channel 1-
7 TMDS Data Channel 0+
8 TMDS Data Channel 0 Shield
9 TMDS Data 0-
10 TMDS Clock+
11 TMDS Clock Shield
12 TMDS Clock-
13 CEC
14 No Connect
15 DDC Clock
16 DDC Data
17 Ground
18 Power (+5V)
19 Hot Plug Detect
2 TMDS Data Channel 2 Shield
3 TMDS Data Channel 2-
4 TMDS Data Channel 1+
5 TMDS Data Channel 1 Shield
6 TMDS Data Channel 1-
7 TMDS Data Channel 0+
8 TMDS Data Channel 0 Shield
9 TMDS Data 0-
10 TMDS Clock+
11 TMDS Clock Shield
12 TMDS Clock-
13 CEC
14 No Connect
15 DDC Clock
16 DDC Data
17 Ground
18 Power (+5V)
19 Hot Plug Detect
The pin configuration of a display panel, such as MIPI used in many LCD or OLED panels, is completely different from standard video inputs like HDMI. Therefore, a controller board is required to convert and transfer the signal from MIPI to HDMI, or vice versa, depending on the application.
Understanding LCD Driver Boards: A Comprehensive Guide
When your LCD screen fails to power on, displays a black/white screen, shows distorted images, or experiences ripple interference, the issue might lie with the LCD driver board. This component is a common culprit behind many LCD display malfunctions.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about LCD driver boards.

1. What Is an LCD Controller Board?
Think of an LCD screen as a dynamic canvas that displays images and videos. The LCD driver board (or LCD controller board) acts as the conductor, translating analog signals into digital signals—or converting one digital signal format into another—to ensure the screen renders content correctly.
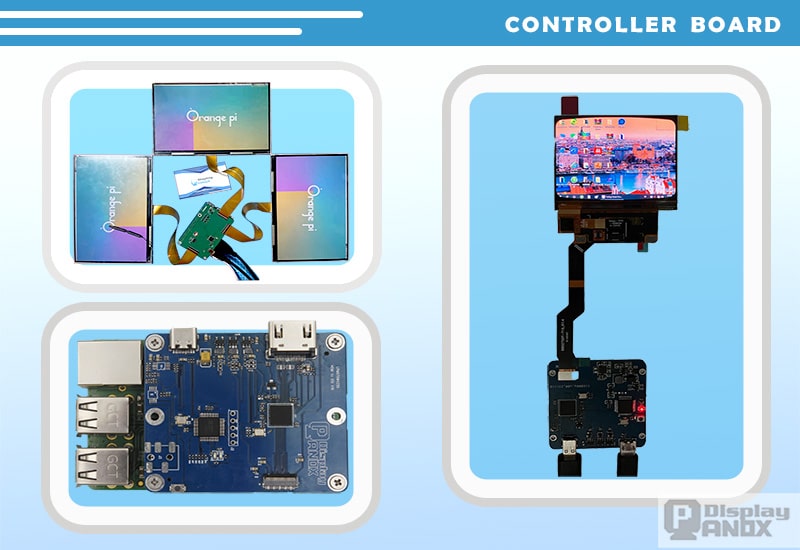
In essence, the driver board serves as the display’s motherboard, also known as the "screen driver." Its primary function is to process input signals and reproduce them on the screen. For example, if connected to a computer, it mirrors the desktop exactly as it appears on the primary monitor.
Panox Display has been supplying LCD and OLED displays for many years. For clients who prefer not to handle the complexities of driving a display panel themselves, we offer customized display controller boards. Our service features competitive pricing, fast development cycles, and quick production turnaround. Click below link to learn more about our custom controller board solutions.
Custom HDMI Controller Board
Custom HDMI Controller Board
2. Key Components of an LCD Controller Board
An LCD driver board typically includes,
Main control chip – The core processor handling signal conversion.
MCU (Microcontroller Unit) – The brain of the display, managing operations.
ROM (Memory) – Stores firmware and configuration data.
Power module – Converts AC (220V) to DC (12V, 5V, 3V, etc.).
Input interfaces (HDMI, VGA, USB-C) – Connects to video sources.
Output interfaces (LVDS, TTL, eDP, MIPI) – Links to the display panel.
Backlight control – Regulates screen brightness (often via OSD buttons).
High-voltage inverter – Powers the backlight (1500–1800V AC).
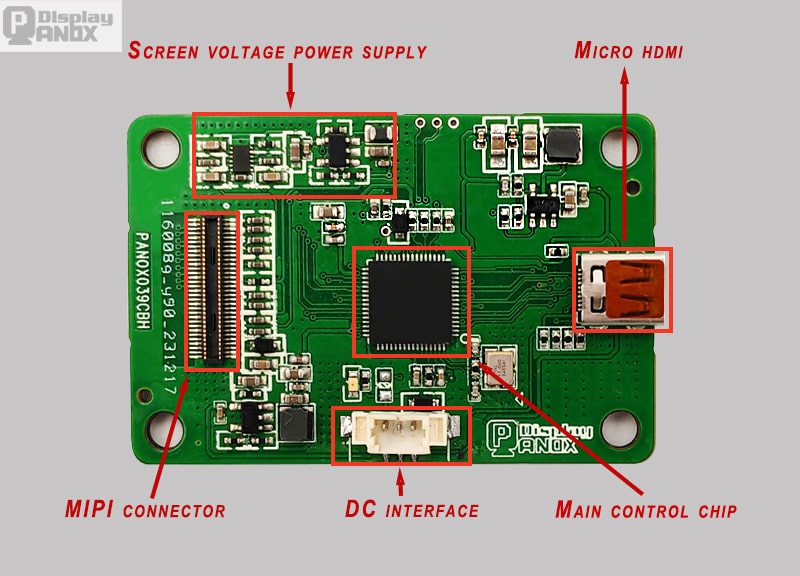
Modern displays frequently combine the power supply and backlight circuits into an integrated "power-inverter combo board" for improved efficiency.
3. Operational Principles of LCD Controller Boards
The controller board performs three essential functions in the signal processing chain:
Signal Reception - Accepts video input signals from source devices (HDMI, VGA, DisplayPort etc.)
Signal Processing - The board's processor interprets signals based on preloaded panel specifications
Signal Conversion - Translates input signals to panel-compatible formats (e.g., HDMI to eDP)
Display Output - Delivers converted signals to the LCD panel for rendering.
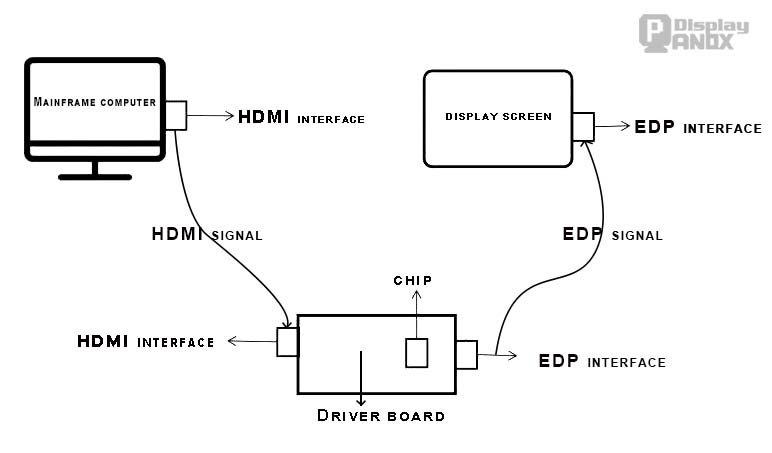
Important Technical Note: The controller board maintains the original signal's resolution and refresh rate throughout the conversion process. A 1080p input signal will output at 1080p resolution regardless of the panel's maximum capabilities.
4. Core Functions of LCD Controller Boards
Power supply: It is like a power adapter for the LCD screen, which converts the external current into the power that the LCD screen can use, such as 5V or 12V.
Receiving signals: It acts as a middleman, receiving the image and video signals sent from the computer or mobile phone.
Common input interfaces include: HDMI, VGA, USB-C
Signal Conversion: This intermediary not only receives signals, but also translates them into a language that the LCD screen can understand.
Common output interfaces include: LVDS, RGB, MIPI, and eDP
Backlight control: It also controls the backlight brightness of the LCD screen to ensure that the picture is clear and bright. It can usually be controlled with an OSD keypad.
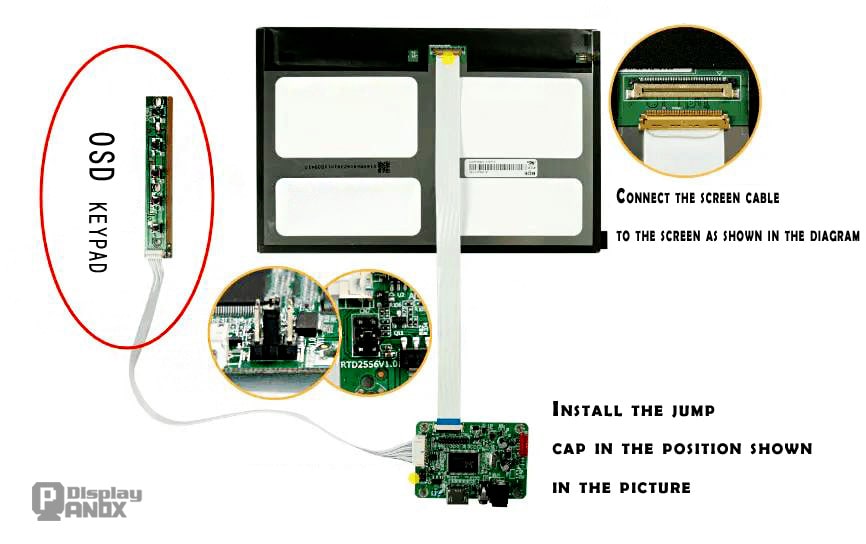
The driver board plays the role of integration and display inside the display. The integration of the LCD driver board is to connect each module inside the display through various interfaces of the output, such as speaker power amplifier, button control, LED strip light, touch pad, battery power supply, etc.
The most important thing of the driver board is the display function, that is, to drive the screen display. The simplest driver board has only one input and output interface to receive and output a display signal to light up the screen.

5. Common Applications Requiring Controller Boards
5.1 When using a bare screen
If you have a bare LCD screen that doesn't have built-in driver circuitry (such as an LCD panel purchased directly from an LCD manufacturer), you'll need a driver board to make it work. Bare screens typically contain only the display panel itself, without any signal processing or power management capabilities.
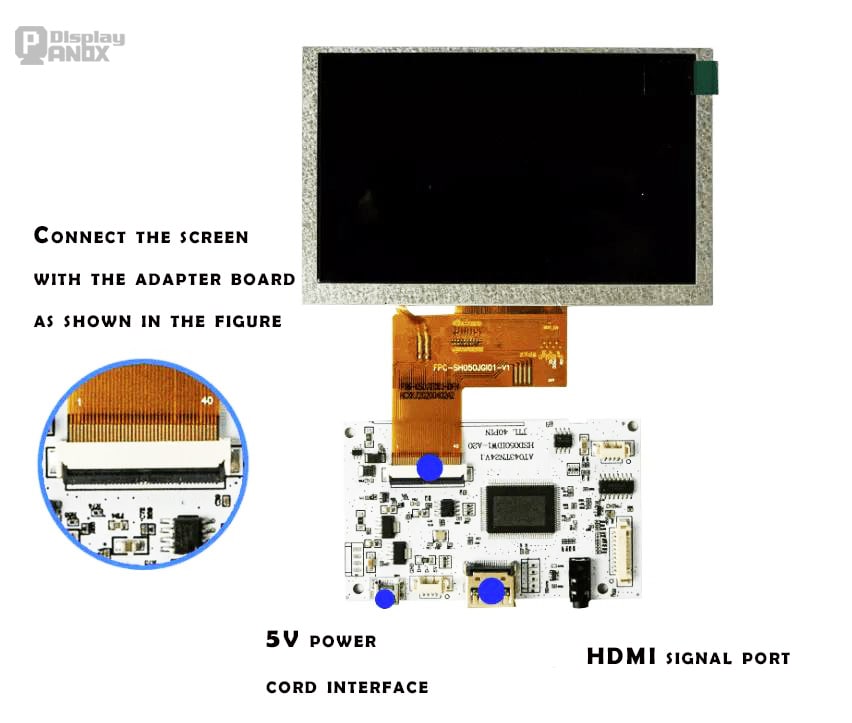
5.2. Add touch function
If your LCD screen has touch panel, the driver board can also process the touch signal and transmit the user's touch actions to the host device.
Related: Get your touch panel from Panox Display
5.3. Provide power management
The driver board can provide stable power management for the LCD screen and other related components, ensuring the stability and reliability of the whole system.
5.4. There is no corresponding LCD screen interface on the motherboard
If there is no interface on the motherboard that directly supports the LCD screen (such as LVDS, EDP, MIPI, etc.), you need to use the LCD driver board. The driver board can convert the signals from other interfaces on the motherboard (such as HDMI, VGA, DVI, etc.) into signal formats that are acceptable to the LCD screen.
6. Technical Selection Standard for Controller Boards
When selecting an LCD controller board, engineers must consider multiple technical factors:
✅ Display Specifications
Native resolution support (1080p, 4K, etc.)
Panel size compatibility (ranging from 5" to 32")
Refresh rate capabilities (60Hz, 120Hz, etc.)
✅ Interface Compatibility
Input interfaces (HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, etc.)
Output interfaces (LVDS, eDP, MIPI, etc.)
✅ Power Requirements
Voltage specifications (5V, 12V, etc.)
Power efficiency considerations
✅ Advanced Features
Touch screen support
On-screen display controls
Image enhancement capabilities
✅ Environmental Considerations
Operating temperature ranges
Humidity tolerance
Vibration resistance
Configuration Example for 15.6" 1080p Display:
Requires controller board with HDMI input/LVDS output
Must support 1920×1080 resolution @ 60Hz
12V DC power compatibility
Integrated backlight control functionality
Conclusion
LCD controller boards serve as critical components across various display applications including,
✅ Medical imaging displays
✅ Industrial control systems
✅ Portable display devices
Proper controller board selection requires thorough evaluation of,
✅ Technical specifications
✅ Interface requirements
✅ Power considerations
✅ Environmental factors
For technical assistance in selecting the optimal controller board solution, consult with our engineering specialists who can provide expert guidance based on your specific application requirements.