LCD Technology: A Reliable Workhorse with Ongoing Enhancements
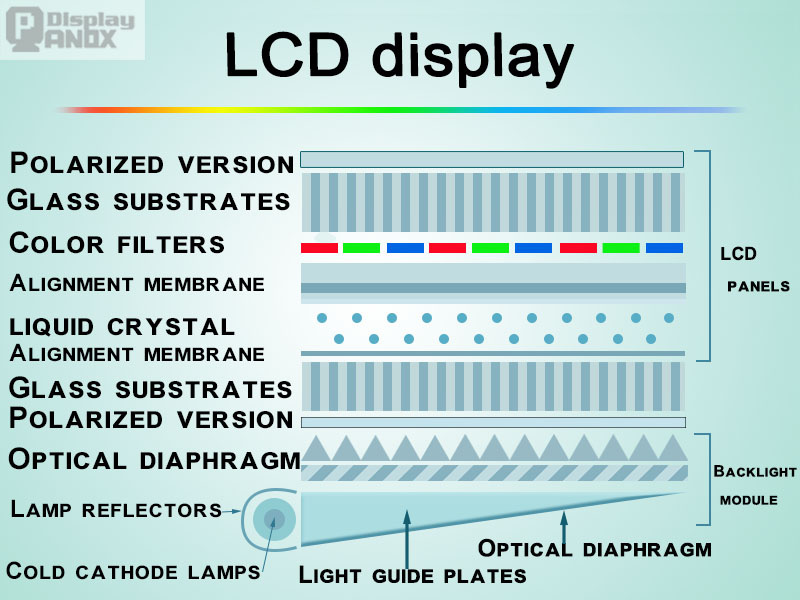
Basic Principle: LCD, or Liquid Crystal Display, is one of the most widely used display technologies today. The Thin Film Transistor (TFT-LCD) is the most common version of LCD, where liquid crystals are sandwiched between two glass substrates. The top glass is a color filter, while the bottom glass substrate contains transistors that control each pixel. When an electric current is applied through the transistors, it changes the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, which modulates the amount of light that passes through, thereby creating color. This principle allows for bright and vibrant displays, which are fundamental for consumer devices like televisions, monitors, and mobile devices.
Market Position: LCD technology is highly mature and remains the most prevalent display technology due to its low cost and reliability. It's found in a wide variety of consumer electronics such as televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones. TFT-LCD is the most common type used in consumer electronics, offering an effective balance between performance and cost. While newer technologies like OLED and Mini LED are gaining ground, LCD continues to be the dominant choice for budget-conscious consumers.

TFT-LCD technology
At present, LCD technology has been quite mature, used in general computer and TV screens, and the cost is low, becoming the basic technology of consumer products..is most commonly used in LCD panels
LED Technology: The Backbone of Modern Displays
Basic Principle: Light Emitting Diodes (LED’s) convert electrical energy into light through semiconductor materials. The process occurs when an electric current flows through the semiconductor, combining electrons and holes, which results in the release of energy in the form of visible light. The wavelength (color) of the light emitted varies depending on the materials used.
Use in Displays:
While "LED" often refers to the backlight in LCD displays, it can also be used as a direct display technology in some cases. In the context of displays, LEDs are typically used for backlighting in modern televisions and monitors, with many of the high-end units using Full Array Local Dimming (FALD) for better contrast. Direct-view LED technology is often seen in large-scale digital signage and outdoor applications.

OLED Technology: Premium Performance and Challenges
Popularity and Performance: OLED technology has cemented itself as a premium display option, particularly for high-end TVs and smartphones in both the U.S. and Europe. In the U.S., OLED is favored for its deep blacks, rich colors, and overall stunning image quality, making it a top choice for home theater setups and gaming monitors. In Europe, OLED TVs are also gaining popularity, especially in markets like Germany and the UK, where consumers prioritize both
performance and sleek, slim designs.
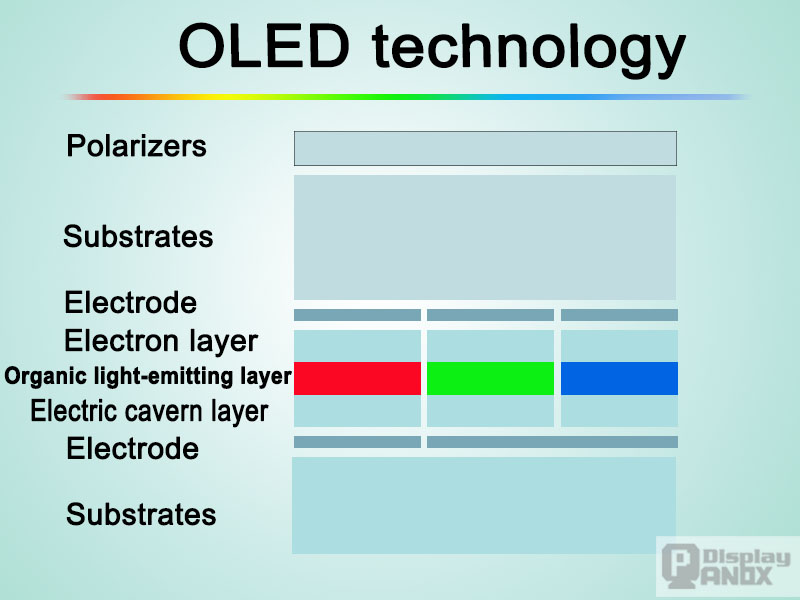
Drawbacks and Longevity: However, OLED ’s susceptibility to burn-in issues is a common topic of discussion in both regions. This is especially important in the U.S. where extended gaming sessions and static images could lead to permanent screen marks. You can mention how, despite its incredible visual performance, OLED still faces challenges in terms of longevity and pricing, limiting its adoption to premium segments.
Applications:
OLED is highly regarded for mobile devices due to its thin form factor and flexible display capabilities. However, it is less common in larger devices, such as TVs, where costs and lifespan issues play a more significant role in consumer decision-making.
Mini LED: Affordable High-Quality Display
Key Differentiation from OLED: Mini LED serves as an excellent middle ground between traditional LCD‘s and OLED displays. In both the U.S. and Europe, consumers appreciate Mini LED for its affordability compared to OLED while still offering significant improvements in brightness, contrast, and HDR effects. In fact, U.S. consumers who seek premium features without the high price tag of OLED often choose Mini
LED, as it brings HDR10+ and Dolby Vision compatibility to more affordable price points.
Multi-Zone Backlight Control: Mini LED’s ability to offer multi-zone backlight control for better contrast and color precision, especially in dark scenes, is a major selling point. This makes it a compelling choice for home entertainment systems. Additionally, its improved local dimming and high peak brightness make it a strong contender in the market, particularly for content that benefits from enhanced HDR capabilities.
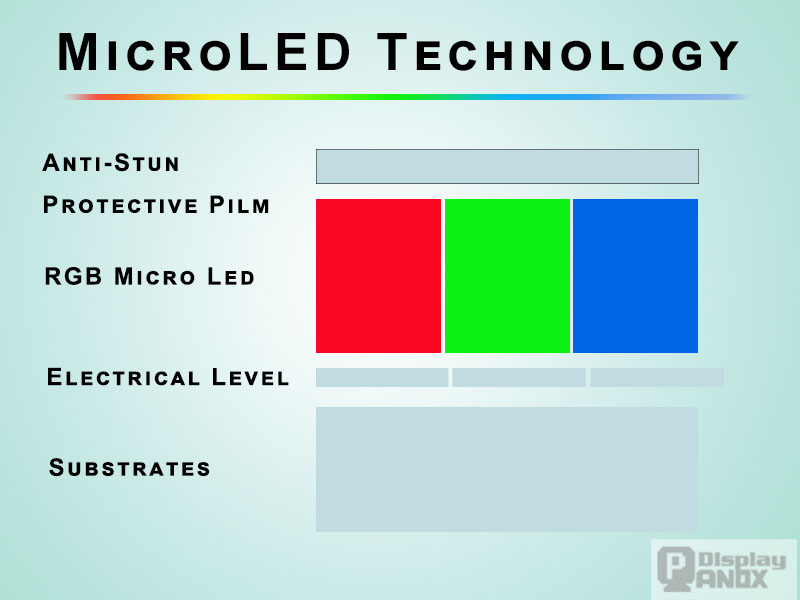
Micro LED: A Revolutionary Step Forward
Future Prospects and Unique Features: Micro LED represents a major technological breakthrough. In the U.S., there’s a lot of excitement surrounding its potential for large-scale, modular displays that can scale up without loss of resolution. This makes Micro LED a top choice for applications like large-format digital signage, AR/VR displays, and even automotive displays. Micro LED’s self-emissive nature, similar to OLED, but without the burn-in problem, makes it an exciting prospect for the future of display technology.
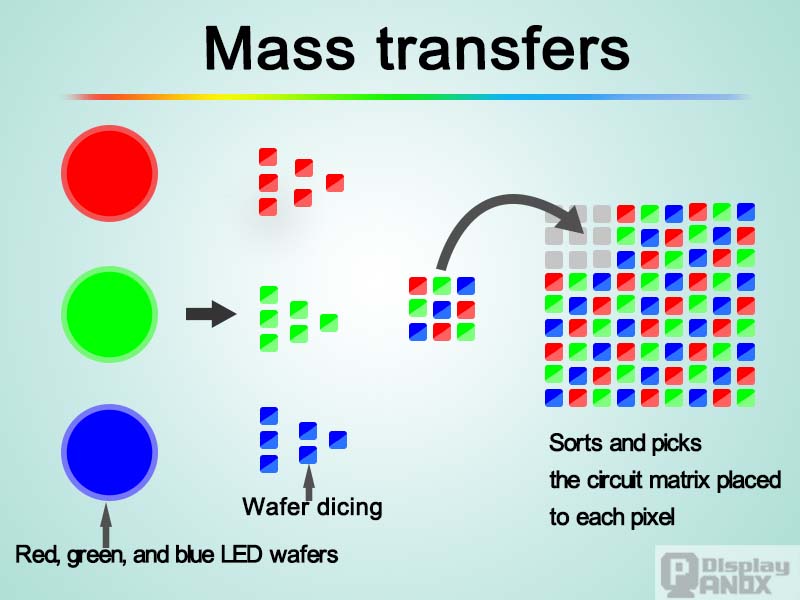
Challenges in Mass Production: While Micro LED’s potential is undeniable, both in Europe and the U.S., challenges in scaling up production remain. The technology's complexities, such as the need for precise placement of tiny LED chips and challenges with yield rates, mean that widespread availability in consumer products is still years away. You can mention the fact that while Micro
LED displays promise significant advancements in visual quality, the market is still waiting for the technological breakthroughs needed to make them affordable and widely available.
Target Markets: Micro LED’s future in wearables, AR/VR devices, and automotive displays is highly anticipated. In the U.S., tech companies like Apple are investing heavily in integrating Micro LED displays in future devices, and it could transform the wearables market with thinner, more energy-efficient displays.
Micro OLED: Compact and Efficient
Miniaturization for Wearables: Micro OLED is particularly relevant for the growing AR/VR and wearable markets in both the U.S. and Europe. The technology’s ability to be built on a monocrystalline silicon wafer allows for ultra-thin, energy-efficient displays that are ideal for small, portable devices. In Europe, where tech consumers are more inclined towards compact, energy-efficient devices, Micro OLED Display is gaining attention for its potential to improve the user experience in wearables like AR glasses and smartwatches.
Energy Efficiency and Visual Quality: One of the major selling points of Micro OLED is its self-emitting nature and low power consumption. This technology could help overcome the limitations of current OLED screens in wearables by offering brighter displays with lower energy usage, which is particularly important for devices that are continuously in use, such as AR/VR headsets.Conclusion
Conclusion
By focusing on specific regional trends and technological innovations, your article can appeal to both European and U.S. markets. Emphasize the practical advantages of Mini LED and Micro LED as alternatives to OLED, while also addressing the unique strengths of each technology in terms of performance, price, and future applications. Adding a section on sustainability and energy efficiency will also resonate with environmentally conscious consumers, particularly in Europe.
If you need further details or references to strengthen the article, feel free to ask!